Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shimo, Michito*; Niwa, Masakazu; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Amano, Kenji; Tonokura, Kenichi*; Tokunaga, Tomochika*
Fukada Chishitsu Kenkyujo Nempo, (22), p.119 - 137, 2021/00
no abstracts in English
 CO
CO on
on  C transfer to plants impacted by below-ground
C transfer to plants impacted by below-ground  CH
CH release
releaseOta, Masakazu; Tanaka, Taku*
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 201, p.5 - 18, 2019/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:16.8(Environmental Sciences) CH
CH released from deep underground radioactive waste disposal facilities can be a belowground source of
released from deep underground radioactive waste disposal facilities can be a belowground source of  CO
CO owing to microbial oxidation of
owing to microbial oxidation of  CH
CH to
to  CO
CO in soils. Environmental
in soils. Environmental  C models assume that the transfer of
C models assume that the transfer of  CO
CO from soil to plant occurs via foliar uptake of
from soil to plant occurs via foliar uptake of  CO
CO . Nevertheless, the importance of
. Nevertheless, the importance of  CO
CO root uptake is not well understood. In the present study, belowground transport and oxidation of
root uptake is not well understood. In the present study, belowground transport and oxidation of  CH
CH were modeled and incorporated into an existing land surface
were modeled and incorporated into an existing land surface  CO
CO model (SOLVEG-II) to assess the importance of root uptake on
model (SOLVEG-II) to assess the importance of root uptake on  CO
CO transfer to plants. Performance of the model in calculating the belowground dynamics of
transfer to plants. Performance of the model in calculating the belowground dynamics of  CH
CH was validated by simulating a field experiment of
was validated by simulating a field experiment of  CH
CH injection into subsoil. The model was then applied to
injection into subsoil. The model was then applied to  C transfer in a hypothetical ecosystem impacted by continuous
C transfer in a hypothetical ecosystem impacted by continuous  CH
CH input from the water table (bottom of one-meter thick soil). In a shallowly rooted ecosystem with rooting depth of 11 cm, foliar uptake of
input from the water table (bottom of one-meter thick soil). In a shallowly rooted ecosystem with rooting depth of 11 cm, foliar uptake of  CO
CO was significant, accounting for 80% of the
was significant, accounting for 80% of the  C accumulation in the leaves. In a deeply rooted ecosystem (rooting depth of 97 cm), where the root penetrated to depths close to the water-table, more than half (63%) the
C accumulation in the leaves. In a deeply rooted ecosystem (rooting depth of 97 cm), where the root penetrated to depths close to the water-table, more than half (63%) the  C accumulated in the leaves was transferred by the root uptake. We found that
C accumulated in the leaves was transferred by the root uptake. We found that  CO
CO root uptake in this ecosystem depended on the distribution of methane oxidation in the soil; all
root uptake in this ecosystem depended on the distribution of methane oxidation in the soil; all  C accumulated in the leaves was transferred by the root uptake when methane oxidation occurred at considerable depths (e-folding depths of 20 cm, or 80 cm). These results indicate that
C accumulated in the leaves was transferred by the root uptake when methane oxidation occurred at considerable depths (e-folding depths of 20 cm, or 80 cm). These results indicate that  CO
CO root uptake contributes significantly to
root uptake contributes significantly to  CO
CO transfer to plants if
transfer to plants if  CH
CH oxidation occurs at great depths and roots penetrate deeply into the soil.
oxidation occurs at great depths and roots penetrate deeply into the soil.
Tamamura, Shuji*; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Aramaki, Noritaka*; Igarashi, Toshifumi*; Kaneko, Katsuhiko*
Groundwater, 56(1), p.118 - 130, 2018/01
Groundwater saturated with gas forms bubble under atmospheric pressure, bothering most authorized methods to determine in-situ dissolved gas concentrations. To circumvent this problem, a simple theory to quantify effect of 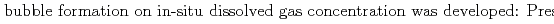 [bar]) of a gas component "
[bar]) of a gas component "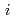 " (e.g., CH
" (e.g., CH , CO
, CO and H
and H ) in equilibrium with in-situ dissolved concentration (
) in equilibrium with in-situ dissolved concentration (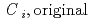 [mol L
[mol L  ]) was related to partial pressure of the
]) was related to partial pressure of the 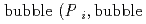 [bar]) emerged from groundwater in the form:
[bar]) emerged from groundwater in the form: 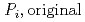 =
= 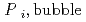 +
+ 
 (k
(k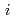 '
' 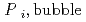 /(
/(
 k
k '
' 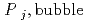 )), where
)), where 
 [bar] is groundwater pressure difference before and after the
[bar] is groundwater pressure difference before and after the 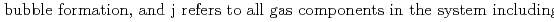 " The k
" The k ' and k
' and k ' corresponds to the Henry's constant [bar L mol
' corresponds to the Henry's constant [bar L mol ] of
] of 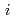 (k
(k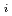 ) and
) and  (k
(k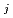 ), respectively, except for k
), respectively, except for k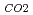 ', which is pH-dependent function. Dissolved CH
', which is pH-dependent function. Dissolved CH concentrations were successfully estimated by the model within the error of
concentrations were successfully estimated by the model within the error of  4.0% from the direct measurements by the sealed sampler method. Similar TIC concentration in the groundwater before and after the rm bubble formation was consistent with the model prediction. The wide application of the model is suggested without selecting sampling locations.
4.0% from the direct measurements by the sealed sampler method. Similar TIC concentration in the groundwater before and after the rm bubble formation was consistent with the model prediction. The wide application of the model is suggested without selecting sampling locations.
Nago, Makito*; Motoshima, Takayuki*; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Kanie, Shunji*; Sanoki, Satoru*
Proceedings of ITA-AITES World Tunnel Congress 2017 (WTC 2017) (USB Flash Drive), 10 Pages, 2017/06
This study presents a new approach to increase construction safety under methane inflow conditions by providing the three-dimensional concentration distribution of methane in underground structures. The study was conducted at the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory, which is located in Neogene sedimentary rock where groundwater contains dissolved methane. As conventional gas sensors are confined to measurement at a single point in time and space, a new system was developed combining a laser methane detector and a laser range finder to effectively obtain the spatial concentration distribution of methane. This system was tested in tunnel galleries located at a depth of 350 m. The results show that this system is effective for identifying unpredicted methane emissions as well as predicted emission hotspots and for examining the validity of the ventilation scheme, which ensures construction safety.
 C monitoring in gaseous radioactive waste
C monitoring in gaseous radioactive wasteUeno, Yumi; Nakagawa, Masahiro; Sato, Junya; Iwai, Yasunori
Hoken Butsuri, 51(1), p.7 - 11, 2016/03
In the Nuclear Science Research Institute, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), in order to oxidize  C, which exists in various chemical forms in exhaust, into
C, which exists in various chemical forms in exhaust, into  CO
CO , a copper oxide (CuO) catalyst is introduced after heating to 600
, a copper oxide (CuO) catalyst is introduced after heating to 600 C. Our goal was to establish a safer
C. Our goal was to establish a safer  C monitoring system by lowering the heating temperature required for the catalyst; therefore, we developed a new hydrophobic palladium/silicon dioxide (Pd/SiO
C monitoring system by lowering the heating temperature required for the catalyst; therefore, we developed a new hydrophobic palladium/silicon dioxide (Pd/SiO ) catalyst that makes the carrier's surface hydrophobic. In these experiments, catalysts CuO, platinum/aluminum oxide (Pt/Al
) catalyst that makes the carrier's surface hydrophobic. In these experiments, catalysts CuO, platinum/aluminum oxide (Pt/Al O
O ), palladium/zirconium dioxide (Pd/ZrO
), palladium/zirconium dioxide (Pd/ZrO ), hydrophobic Pd/SiO
), hydrophobic Pd/SiO , and hydrophilic Pd/SiO
, and hydrophilic Pd/SiO were ventilated with standard methane gas, and we compared the oxidation efficiency of each catalyst at different temperatures. As a result, we determined that the hydrophobic Pd/SiO
were ventilated with standard methane gas, and we compared the oxidation efficiency of each catalyst at different temperatures. As a result, we determined that the hydrophobic Pd/SiO catalyst had the best oxidation efficiency. By substituting the currently used CuO catalyst with the hydrophobic Pd/SiO
catalyst had the best oxidation efficiency. By substituting the currently used CuO catalyst with the hydrophobic Pd/SiO catalyst, we will be able to lower the working temperature from 600
catalyst, we will be able to lower the working temperature from 600 C to 300
C to 300 C and improve the safety of the monitoring process.
C and improve the safety of the monitoring process.
Hoshikawa, Akinori; Igawa, Naoki; Yamauchi, Hiroki; Ishii, Yoshinobu
Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 66(10), p.1810 - 1814, 2005/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:26.14(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Hoshikawa, Akinori; Igawa, Naoki; Yamauchi, Hiroki; Ishii, Yoshinobu; Stern, L. A.*
Proceedings of 5th International Conference on Gas Hydrates (ICGH-5), Volume 5, p.1619 - 1626, 2005/06
no abstracts in English
Igawa, Naoki; Ishii, Yoshinobu; Hoshikawa, Akinori; Yamauchi, Hiroki; Shimoyama, Tomotaka
JAERI-Tech 2004-067, 23 Pages, 2004/11
We synthesized methane hydrate using fine grain ice. The amount of released-gas volume was the same as calculated one for ideal methane hydrate within experimental precision. The neutron diffraction measurement was conducted by means of a high-resolution powder diffractometer (HRPD) installed at JRR-3. No reflection line from the impurities and ice was found in the diffraction pattern. Therefore, the synthesized methane hydrate proved to be very high quality. We also showed the scattering density map of this sample using Rietveld analysis and the maximum entropy method (MEM).
Ishiyama, Shintaro
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 2(1), p.14 - 23, 2003/01
no abstracts in English
Ishiyama, Shintaro
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 44(12), p.879 - 881, 2002/12
no abstracts in English
 , C
, C H
H , C
, C H
H , C
, C H
H , C
, C H
H , and C
, and C H
H
Shirai, Toshizo; Tabata, Tatsuo*; Tawara, Hiroyuki*; Ichikawa, Yukikazu*
Atomic Data and Nuclear Data Tables, 80(2), p.147 - 204, 2002/03
Times Cited Count:74 Percentile:93.82(Physics, Atomic, Molecular & Chemical)Cross sections for 138 processes of hydrocarbons in collisions with electrons, based on available literature sources, are critically compiled. The leterature has been surveyed to September 2000. A short comment is given for each measurement. The recommended data sets are presented in separate graphs for each process. Analytic fits to the recommended cross sections are also presented.
Ogawa, Masuro
Enerugi, 34(5), p.81 - 87, 2001/05
no abstracts in English
Ohashi, Hirofumi; Sakaki, Akihiro; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki
JAERI-Research 2000-058, 64 Pages, 2001/01
no abstracts in English
 , CO
, CO and N
and N O in Tokai-mura
O in Tokai-muraPorntepkasemsan, B.*; Atarashi-Andoh, Mariko; Amano, Hikaru
JAERI-Data/Code 2000-032, 43 Pages, 2000/11
no abstracts in English
Amano, Hikaru; Porntepkasemsan, B.; Atarashi-Andoh, Mariko; Kushita, Kohei
KURRI-KR-53, p.6 - 9, 2000/09
no abstracts in English
Mine, Tatsuya*; Mihara, Morihiro;
JNC TN8430 2000-010, 27 Pages, 2000/07
In the geological disposal system of the radioactive wastes, gas generation by microorganism could be significant for the assessment of this system, because organic material included in groundwater, buffer material and wastes might serve as carbon sources for microorganisms. In this study, gas generation tests using microorganisms were carried out under anaerobic condition. The amount of methane and carbon dioxide that were generated by activity of Methane Producing Bacteria (MPB) were measured with humic acid, acetic acid and cellulose as carbon sources. The results showed that methane was not generated from humic acid by activity of MPB. However, in the case of using acetic acid and cellulose, methane was generated, but at high pH condition (pH=10), the amount of generated methane was lower than at low pH (pH=7). It was not clear whether the pH would affect the amount of generated carbon dioxide.
 emission
emissionFumizawa, Motoo; *; Yamada, Seiya*
Enerugi, Shigen, 20(1), p.87 - 92, 1999/01
no abstracts in English
Miyamoto, Yoshiaki; Shiozawa, Shusaku; Ogawa, Masuro; Akino, Norio; Shimizu, Saburo; Hada, Kazuhiko; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Onuki, Kaoru; Takeda, Tetsuaki; Nishihara, Tetsuo
IAEA-TECDOC-1056, p.191 - 200, 1998/11
no abstracts in English